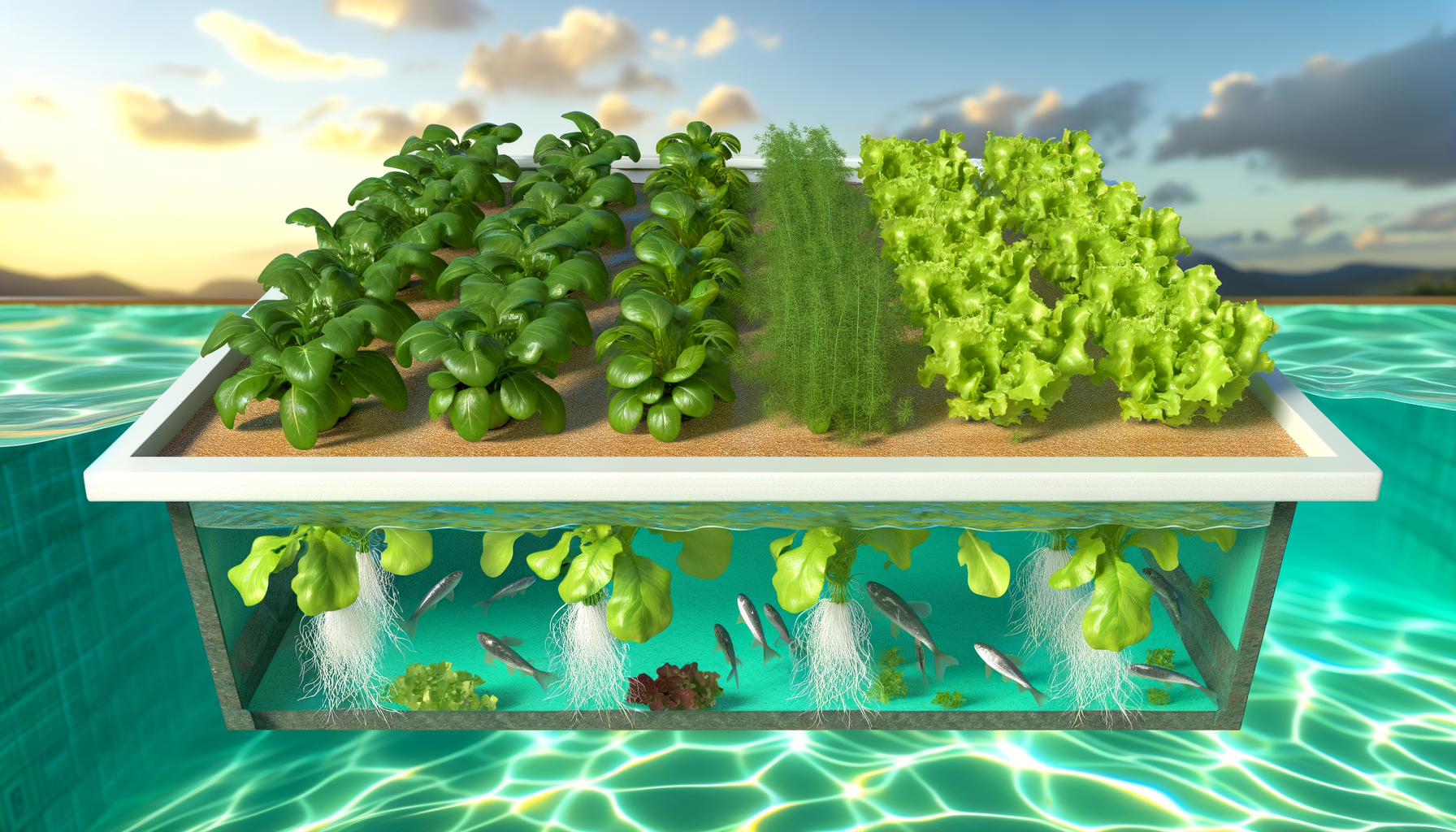
Introduction to Aquaponics Grow Bed Depth
Overview of Aquaponics Systems
Aquaponics is an innovative and sustainable method of agriculture that combines aquaculture (raising fish) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil) into a single integrated system. In this symbiotic arrangement, fish waste provides an organic nutrient source for the plants, while the plants help to filter and purify the water, which is then recirculated back to the fish tanks. This creates a closed-loop system that is efficient in water usage and can produce both protein in the form of fish and fresh produce without the need for synthetic fertilizers or pesticides.
Significance of Grow Bed Depth
The heart of an aquaponics system is the grow bed, where plants are cultivated. The depth of the grow bed is a critical factor that influences the overall health and productivity of the system. It affects the root development of plants, the efficiency of nutrient filtration, and the oxygenation of the water. A well-designed grow bed depth accommodates the specific needs of the plants being grown, supports the biological filtration necessary to convert fish waste into plant-available nutrients, and ensures adequate water flow and oxygenation for both plants and fish. For instance, a 12-inch deep grow bed, such as the Aquaponics Easy-Reach 50 Gallon Grow Bed, is often ideal for a variety of plant species, providing ample space for root growth and effective nutrient uptake.
Objective of the Article
The objective of this article is to explore the best grow bed depth for aquaponics systems, considering the needs of both plants and fish. We will delve into the functions of the grow bed, the key factors that influence the choice of depth, and the advantages and disadvantages of different depths. By the end of this article, readers will be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions about the design of their aquaponics grow beds, ensuring the health and productivity of their systems. Whether you are a hobbyist or a commercial farmer, understanding grow bed depth is essential for the success of your aquaponics venture.
html
Understanding Grow Bed Functions
Nutrient Filtration and Plant Support
The grow bed in an aquaponics system is not just a container for growing media; it is a dynamic ecosystem that plays a critical role in the health and productivity of the plants. One of its primary functions is nutrient filtration. As water from the fish tank flows through the grow bed, the plants absorb essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are derived from fish waste. This process not only provides the plants with the sustenance they need to grow but also cleans the water by removing these compounds, which can be toxic to fish at high levels. The grow media within the beds also offers physical support for the plants, anchoring roots and giving them a stable environment to develop. Additionally, the media houses beneficial bacteria that play a vital role in the nitrification process, further purifying the water for the fish.
Root Zone and Oxygenation
The root zone is a critical area within the grow bed where the roots of the plants reside. In aquaponics, the health of the root zone is paramount, as it is the primary site for nutrient uptake. The design of the grow bed must ensure that the roots have access to both water and air; thus, the depth of the grow bed must be sufficient to allow for a healthy balance between moisture and oxygenation. As water ebbs and flows through the grow bed, it not only delivers nutrients but also oxygenates the root zone, which is essential for preventing anaerobic conditions that can harm plant roots and disrupt nutrient uptake.
Impact on System Balance
The depth of the grow bed has a significant impact on the overall balance of the aquaponics system. A well-designed grow bed depth contributes to the homeostasis of the aquaponic ecosystem by ensuring efficient nutrient filtration, providing adequate space for root development, and facilitating proper water and oxygen distribution. It is a balancing act that requires careful consideration of the types of plants being grown, the fish species, and the specific environmental conditions of the system. The depth must be tailored to support the symbiotic relationship between the fish, plants, and bacteria, ultimately leading to a sustainable and productive aquaponics system.
Key Factors Influencing Grow Bed Depth
Plant Types and Root Systems
The types of plants you plan to grow in your aquaponics system play a pivotal role in determining the optimal grow bed depth. Leafy greens such as lettuce, kale, and Swiss chard have relatively shallow root systems and thrive in grow beds that are 6 to 12 inches deep. This depth allows for efficient nutrient uptake and rapid growth cycles. On the other hand, fruiting plants like tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers require deeper grow beds, typically 12 to 18 inches or more, to accommodate their extensive root systems and higher nutrient demands. The depth must be sufficient to prevent root crowding and ensure that plants can access the nutrients they need without competition.
Fish Species and Waste Production
The species of fish in your aquaponics system and their waste production significantly influence grow bed depth. Fish such as tilapia and catfish are known for their high nutrient output, which can be well-suited for shallower grow beds where plants can readily absorb these nutrients. Conversely, fish that produce less waste may necessitate deeper grow beds to ensure that plants receive an adequate supply of nutrients. It’s essential to find a balance that supports both the fish and plant components of your system.
Climate and Environmental Conditions
Local climate and environmental conditions are critical factors to consider when selecting grow bed depth. In regions with high temperatures and strong evaporation rates, deeper grow beds can help retain moisture and provide thermal stability to the root zone. In contrast, shallower grow beds may be more appropriate in cooler climates as they can warm up more quickly and are less prone to over-watering. Understanding and adapting to your specific environmental conditions will help ensure the success of your aquaponics system.
Space Availability and Budget Constraints
Practical considerations such as the space you have available and your budget can also dictate the depth of your grow beds. If space is at a premium, shallower grow beds may be necessary to maximize plant production within a limited area. However, if you have more room to work with, deeper beds can offer the flexibility to grow a wider variety of plants. Budget constraints are equally important; deeper grow beds require more grow media and a stronger support structure, which can increase initial costs. Conversely, shallow beds are generally more cost-effective but may limit the diversity of plants you can grow. Balancing these practical considerations is crucial for creating a sustainable and productive aquaponics system.
Pros and Cons of Different Grow Bed Depths
Shallow Grow Beds (6-12 inches)
Pros:
- Efficient Water Use: Shallow grow beds are highly water-efficient, requiring less water for saturation, which is ideal for regions with water scarcity or where water conservation is a priority.
- Quick Plant Growth: These beds provide rapid nutrient absorption for plants with shallow root systems, such as leafy greens, resulting in faster growth and more frequent harvests.
- Ease of Maintenance: Shallow beds are easier to maintain due to less growing medium and lower water volumes, reducing maintenance time and effort.
Cons:
- Limited Plant Variety: Shallow beds may not support plants with deep root systems or high nutrient demands, restricting the variety of crops you can grow.
- Frequent Watering: Due to limited water-holding capacity, shallow beds may require more frequent watering, which can be demanding in terms of time and resources.
Medium-depth Grow Beds (12-18 inches)
Pros:
- Versatility: Medium-depth grow beds offer a balance between shallow and deep options, allowing for a broader range of plant choices, including both leafy greens and fruiting plants.
- Stable Nutrient Supply: With a greater nutrient buffer, these beds can provide a consistent supply of nutrients, reducing the risk of deficiencies and promoting healthy growth.
- Moderate Water Use: They strike a reasonable balance between water efficiency and plant diversity, making them suitable for various climates and purposes.
Cons:
- Initial Costs: Setting up medium-depth beds can be costlier than shallow beds due to the need for more growing medium and infrastructure.
- Maintenance: They may require more attention compared to shallow beds, especially in terms of monitoring nutrient levels and water quality.
Deep Grow Beds (18+ inches)
Pros:
- Plant Diversity: Deep grow beds provide ample space for a variety of plants, including those with extensive root systems or high nutrient demands, such as tomatoes and peppers.
- Reduced Watering Frequency: The larger water-holding capacity of deep beds reduces the need for frequent watering, which is beneficial in regions with high temperatures or low humidity.
- Nutrient Stability: Deeper beds offer better nutrient stability, making them suitable for long-term and larger-scale aquaponics systems.
Cons:
- Increased Water Consumption: While deep beds can reduce watering frequency, they may use more water overall, which could be a concern in water-scarce regions.
- Higher Initial Investment: Creating and maintaining deep grow beds can be more expensive, requiring additional growing medium and robust support structures.
- Slower Plant Growth: For shallow-rooted plants, deep beds may lead to slower growth due to the extended distance nutrients need to travel.
Strategies for Determining the Ideal Grow Bed Depth
Aligning Plant and Fish Needs
When determining the ideal grow bed depth for an aquaponics system, it is crucial to align the needs of both the plants and the fish. The type of fish and their waste production rate will influence the nutrient availability in the water, which in turn affects plant growth. Fish species such as tilapia and catfish, known for higher waste output, may be well-suited to shallower beds that allow plants to absorb nutrients more efficiently. Conversely, ornamental fish with lower waste production may necessitate deeper beds to ensure adequate nutrient levels for plant growth.
Additionally, the choice of plants is paramount. Leafy greens with shallow root systems thrive in shallower beds, while fruiting plants with deeper roots require more depth to access nutrients effectively. It is essential to consider the balance between plant types and select a grow bed depth that accommodates both shallow and deep-rooted plants if diversity in crop production is desired.
Adapting to Climate and Environmental Factors
Climate and local environmental conditions significantly impact the decision on grow bed depth. In areas with high evaporation rates and warmer temperatures, deeper grow beds can help retain moisture and provide thermal stability. In contrast, shallower beds may be more appropriate in cooler climates as they warm up more quickly and are less prone to overwatering.
Environmental factors such as humidity, wind, and sunlight exposure also play a role. A deeper grow bed might be beneficial in windy areas to prevent rapid drying, while in high humidity areas, shallower beds could reduce the risk of root rot and other moisture-related diseases. Understanding these local factors is essential for choosing a grow bed depth that will support a robust and productive aquaponics system.
Considering Space and Budget Limitations
Space availability and budget constraints are practical considerations that can influence grow bed depth. In urban settings or areas with limited space, shallower beds may be more feasible, allowing for a higher density of plant growth within a smaller footprint. For those with more space, deeper beds offer the flexibility to grow a wider variety of plants and can support larger root systems.
The budget also plays a significant role in determining grow bed depth. Shallow beds require less grow media and infrastructure, making them more cost-effective and accessible for beginners or those with limited financial resources. On the other hand, deeper beds involve a higher initial investment due to the increased amount of grow media and the need for more robust support structures.
Ultimately, the ideal grow bed depth is a balance between the biological needs of the plants and fish, the local environmental conditions, and the practical limitations of space and budget. By carefully considering these factors, aquaponics enthusiasts can optimize their systems for maximum productivity and sustainability.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Grow Bed Performance
Water Quality Management
Maintaining pristine water quality is paramount in aquaponics, as the health of both fish and plants hinges on it. Regular testing of pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels is essential. Aim to keep the pH between 6.5 and 7.5 for optimal nutrient uptake and fish health. Ammonia and nitrite levels should be near zero, while nitrates, the end product of the nitrification process, should be present but controlled. Regular water changes and the use of biofilters can help maintain these parameters. Additionally, monitoring dissolved oxygen levels ensures that both fish and beneficial bacteria have enough oxygen to thrive, which is particularly crucial in deeper grow beds.
Regular Monitoring and System Adjustments
Consistent monitoring allows for timely adjustments to maintain system balance. Keep an eye on water temperature, as extreme temperatures can stress fish and affect plant growth. Use heaters or coolers as needed. Inspect plant health regularly for signs of nutrient deficiencies or disease, and adjust feeding rates or supplement with nutrients accordingly. System flow rates should also be checked to ensure that water is evenly distributed throughout the grow bed, preventing dry spots or waterlogging.
Ensuring Plant and Fish Health
Healthy plants and fish are the indicators of a well-functioning aquaponics system. For plants, ensure they are receiving adequate light and are not overcrowded. Prune dead leaves and manage pests using organic methods to prevent disease spread. For fish, observe their behavior and appearance for signs of stress or illness. Quarantine new fish before introducing them to the system to prevent the spread of disease. Feed high-quality food in appropriate quantities to prevent waste build-up, which can lead to poor water quality.
In conclusion, diligent maintenance and proactive management are the keys to sustaining an efficient aquaponics system. By focusing on water quality, regular monitoring, and the health of your plants and fish, you can ensure that your grow bed performs optimally, leading to a bountiful and healthy harvest.
Conclusion
Summary of Grow Bed Depth Considerations
In the pursuit of a flourishing aquaponics system, the depth of the grow bed emerges as a critical factor. It influences not only the health and yield of the plants but also the overall balance and efficiency of the ecosystem. Throughout this article, we have explored the multifaceted role of grow beds, from nutrient filtration and plant support to root zone health and oxygenation. We’ve delved into the key factors that dictate the optimal depth for grow beds, such as the types of plants and their root systems, the fish species and their waste production, as well as the local climate and environmental conditions.
Moreover, we have weighed the advantages and disadvantages of shallow, medium-depth, and deep grow beds, providing insights into how each can serve different purposes within an aquaponics system. Shallow beds are ideal for leafy greens and are more water-efficient, while deeper beds cater to the needs of fruiting plants and offer greater nutrient stability. The choice between these options is also influenced by practical considerations like space availability and budget constraints.
Final Thoughts on Personalizing Grow Bed Depth
Ultimately, the best grow bed depth is not a universal standard but a personalized decision that should be tailored to the unique requirements of your aquaponics system. It is a balance between the biological needs of your plants and fish, the physical constraints of your environment, and the practicalities of your resources. To achieve this balance, it is essential to align the plant and fish needs, adapt to climate and environmental factors, and consider space and budget limitations.
Maintaining optimal grow bed performance is an ongoing process that involves diligent water quality management, regular monitoring, and system adjustments. It is crucial to ensure that the water is appropriately oxygenated, pH levels are stable, and nutrient levels are adequate for plant growth. Keeping a close eye on the health of both plants and fish will help in early detection and management of potential issues.
In conclusion, the journey to determining the ideal grow bed depth is one of experimentation and learning. By understanding the principles outlined in this article and applying them to your system, you can create a thriving aquaponics garden that is both productive and sustainable. Remember, the key to success lies in personalizing your grow bed depth to fit the unique tapestry of your aquaponic aspirations.




