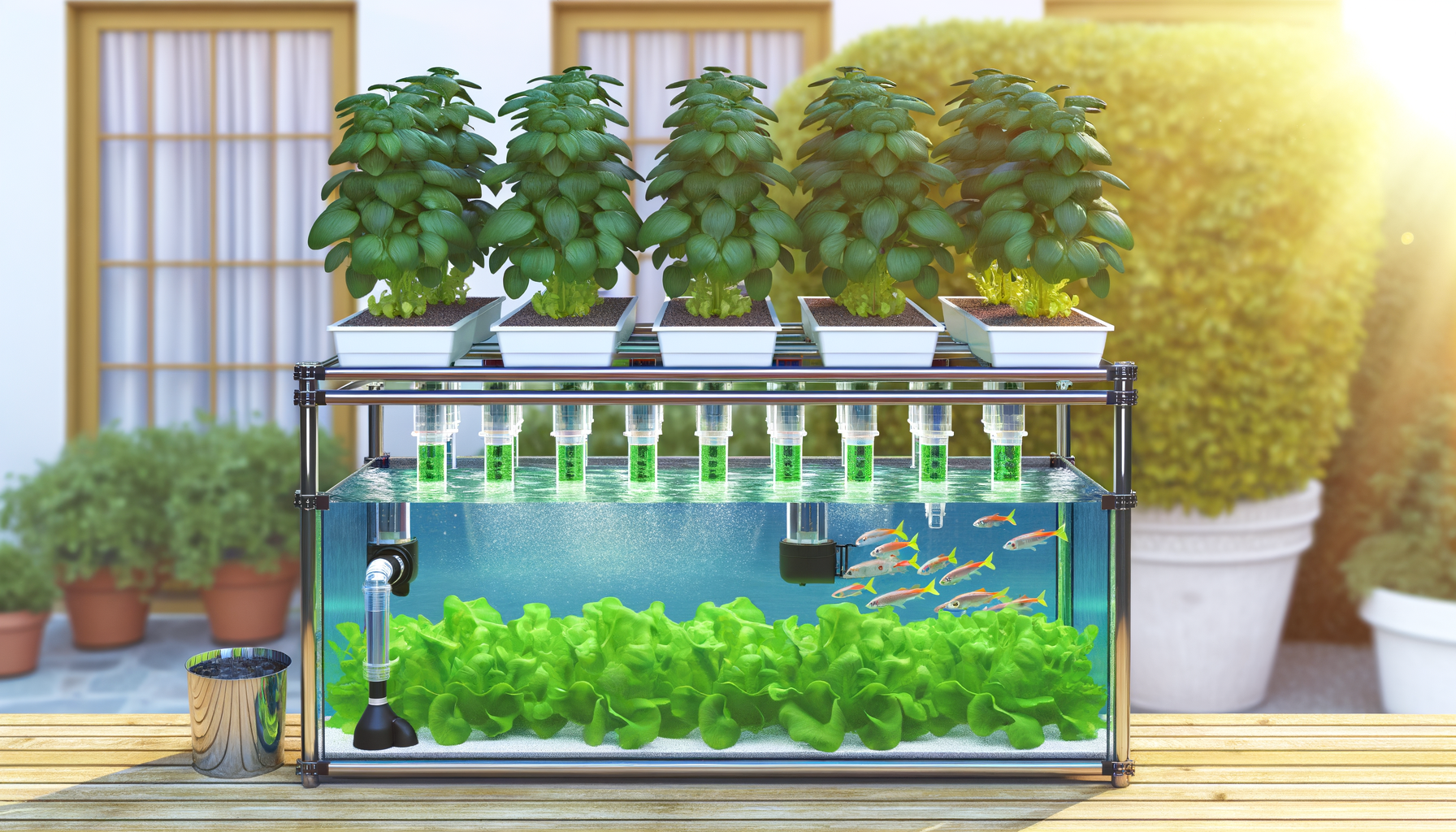
Introduction to Aquaponics
What is Aquaponics?
Aquaponics is an innovative and sustainable method of growing food that marries aquaculture (the raising of fish) with hydroponics (the soilless cultivation of plants). This symbiotic relationship forms a closed-loop system where fish waste provides an organic nutrient source for the plants, and the plants, in turn, purify the water for the fish. This creates a harmonious environment where both fish and plants can thrive.
Benefits of Aquaponics
The benefits of aquaponics are manifold. It is a highly sustainable form of agriculture that uses up to 90% less water than traditional farming methods. Aquaponics systems can yield a high output of both fish and plants in a relatively small space, making it ideal for urban environments or areas with limited agricultural land. Additionally, because the system is closed and recycles water, it conserves resources and reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, offering a fresh and nutritious produce that is free from harmful contaminants. The ability to grow food year-round, regardless of external weather conditions, and the cost savings associated with reduced water and fertilizer use, make aquaponics an attractive option for sustainable food production.
Key Components of an Aquaponics System
An aquaponics system is comprised of several key components that work together to support the life within it. These include the fish tank, which houses the fish; the grow bed, where plants are cultivated; water and air pumps to circulate water and oxygenate it; tubing and fittings for connecting system elements; grow media to support plant roots and beneficial bacteria; and aeration equipment to ensure adequate oxygen levels. Optional components such as grow lights, heaters, and monitoring systems can also be included to optimize the environment for both fish and plants.
Understanding the Role of Equipment
The equipment in an aquaponics system is not merely functional; it is the backbone that supports the entire ecosystem. Each piece of equipment plays a critical role in maintaining the delicate balance required for the system to function effectively. Water pumps ensure the movement of nutrients from fish to plants, while air pumps and aerators provide the oxygen vital for fish survival and beneficial bacterial growth. Grow lights and heaters may be used to simulate ideal environmental conditions, and monitoring systems allow for the precise control of factors such as pH, temperature, and nutrient levels. Understanding how each component functions and interacts with others is essential for the success and productivity of an aquaponics system.
The Heart of the System: Water Pumps
Types of Water Pumps
Water pumps in aquaponics systems are pivotal for maintaining a healthy environment for both fish and plants. They are responsible for circulating water throughout the system, ensuring that nutrients reach the plants and that the water remains oxygenated for the fish. There are two primary types of water pumps used in aquaponics:
- Submersible Pumps: These are placed directly in the water, typically in the fish tank. They are known for their quiet operation and ease of installation. Submersible pumps are ideal for smaller systems and indoor setups where noise levels are a concern.
- External Pumps: Also known as inline pumps, these are installed outside of the water tanks. They are typically more powerful than submersible pumps and are used in larger aquaponics systems. External pumps require more complex plumbing but offer easier maintenance access.
Determining the Right Pump Size
Choosing the correct size for your water pump is critical for the efficiency of your aquaponics system. The pump must be capable of circulating the entire volume of water in your system at least every two hours. To determine the right pump size, consider the following:
- Calculate the total water volume of your system, including all tanks and sumps.
- Desired flow rate: Aim for a flow rate that is 2 – 4 times the volume of your tank per hour, depending on the needs of your plants and fish.
- Head height: Measure the vertical distance from the water level in your fish tank to the highest point of water delivery. This affects the pump’s flow rate.
- Pipe diameter: Ensure the diameter of your pipes can handle the flow rate without causing restrictions.
It’s also wise to select a pump with a slightly higher flow rate than needed to account for any loss due to filtration or pipe bends.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Regular maintenance of your water pump is essential to prevent failures that could jeopardize your aquaponics system. Here are some tips to keep your pump running smoothly:
- Clean the intake filter: Regularly inspect and clean the pump’s intake filter to prevent clogs from debris.
- Inspect the impeller: Check the impeller for blockages or damage and clean or replace as necessary.
- Check for leaks: Examine the pump and its connections for any signs of leaks and address them promptly.
- Monitor performance: Keep an eye on the pump’s flow rate and noise level. Any changes could indicate a problem that needs attention.
- Consider a pre-filter: For external pumps, a pre-filter can help reduce the amount of debris that reaches the pump, extending its lifespan.
By understanding the types of water pumps available, determining the right size for your system, and adhering to a regular maintenance schedule, you can ensure that the heart of your aquaponics system remains healthy and efficient.
Fish Tanks: Creating a Healthy Habitat
Choosing the Right Tank Size
When setting up an aquaponics system, selecting the appropriate fish tank size is crucial for the well-being of the fish and the overall balance of the ecosystem. The tank should provide ample space for fish to grow and thrive, as overcrowding can lead to stress and disease. A general rule of thumb is to provide at least 1 gallon of water for every 1 inch of fish at maturity. Consider the growth rate and adult size of the species you plan to raise, as well as the system’s total plant growing area, to determine the ideal tank volume.
Material Considerations for Tanks
The material of your fish tank impacts the health of your fish and the durability of your system. Common materials include food-grade polyethylene, fiberglass, and glass. Food-grade polyethylene is lightweight, affordable, and resistant to UV light, making it a popular choice. Fiberglass tanks are robust and long-lasting but can be more expensive. Glass tanks offer excellent visibility but are heavy and can be prone to cracking. Avoid materials that may leach harmful substances into the water, such as certain metals or plastics not intended for aquatic use.
Temperature and Filtration Needs
Maintaining the correct water temperature is essential for fish health. Each species has its preferred temperature range, and it’s important to equip your system with heaters or chillers as needed to keep the water within this range. Filtration is equally important; a good filtration system will remove solid waste and convert ammonia from fish waste into nitrates, which plants can use. This biological filtration is typically achieved through a combination of a mechanical filter to remove solids and a biofilter to house nitrifying bacteria. Regular monitoring and maintenance of temperature and filtration systems are key to creating a healthy habitat for your fish.
“`
Grow Beds and Media: Plant Nutrition and Support
Types of Grow Beds
Grow beds are the foundation of plant growth in an aquaponics system, serving as the site where plants absorb essential nutrients from the water. There are several types of grow beds to consider:
- Media-Based Grow Beds: These are filled with a solid growing medium like gravel or expanded clay pellets. They support plant roots and house beneficial bacteria that convert fish waste into plant-available nutrients.
- Floating Raft Beds: Also known as Deep Water Culture (DWC), plants are placed in floating boards with roots suspended directly in the nutrient-rich water, allowing for efficient nutrient uptake.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) Beds: In NFT systems, a thin film of water flows through channels, providing roots with constant access to nutrients and oxygen.
Each type of grow bed has its own advantages and is suitable for different plant types and system sizes.
Selecting the Appropriate Grow Media
The grow media not only supports the plants physically but also plays a crucial role in the biological filtration of the aquaponics system. When selecting grow media, consider:
- Porosity: Media should be porous enough to host beneficial bacteria that are vital for nutrient cycling.
- Weight: Lightweight media like expanded clay pebbles are easier to handle and less likely to compress plant roots.
- pH Neutral: The media should not alter the pH of the water, ensuring a stable environment for both fish and plants.
- Non-Toxic: Ensure the media is inert and free from substances that could harm the fish or plants.
Common choices for grow media include expanded clay pellets, lava rock, and gravel, each with its own set of benefits.
Managing Nutrient Delivery
Effective nutrient delivery is critical for plant health and growth in an aquaponics system. Here are key considerations for managing nutrient delivery:
- Nutrient Cycling: Establish a robust nitrogen cycle by ensuring a healthy population of beneficial bacteria to convert fish waste into nitrates, the primary nutrient for plants.
- Water Flow: Maintain a consistent water flow to ensure nutrients are evenly distributed throughout the grow bed, preventing areas of nutrient deficiency or toxicity.
- Plant Selection: Choose plants that are compatible with the nutrient levels produced by your fish. Leafy greens, for example, thrive in aquaponics systems due to their lower nutrient requirements compared to fruiting plants.
- Monitoring: Regularly test water for pH, ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates to maintain optimal levels for plant uptake and fish health.
By carefully managing these factors, you can ensure your plants receive the right balance of nutrients to grow vigorously while also purifying the water for the fish.
Water Quality Management
Importance of Water Quality
The lifeblood of any aquaponics system is its water. The quality of water affects every aspect of the ecosystem, from the health of the fish to the growth of the plants. High-quality water ensures that fish are healthy, stress-free, and producing the waste necessary for plant nutrition. Conversely, poor water quality can lead to fish diseases, plant nutrient deficiencies, and ultimately, system failure. Therefore, maintaining pristine water conditions is not just beneficial but essential for the success of an aquaponics system.
Monitoring pH and Nutrient Levels
Monitoring the pH level of the water is critical, as it affects nutrient availability and the health of both fish and plants. The ideal pH range for most aquaponic systems is between 6.8 and 7.2. Regular testing and adjustments, if necessary, help maintain this balance. Nutrient levels, particularly nitrogen compounds like ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates, must also be monitored closely. Ammonia and nitrites are toxic to fish even at low levels, while nitrates, though less harmful, can indicate an imbalance if they accumulate excessively.
Aeration and Oxygenation Equipment
Aeration is vital for maintaining oxygen levels in the water, which fish need to survive. Oxygenation also benefits the root systems of plants, allowing for better nutrient uptake and growth. Equipment such as air pumps and air stones are commonly used to introduce oxygen into the water. The size and capacity of the aeration system should match the needs of the fish population and the volume of water in the system.
Solutions for Common Water Quality Issues
- Ammonia Buildup: This can be addressed by reducing feed rates, increasing aeration, and ensuring the biofilter is adequately sized and functioning correctly.
- Algae Growth: Algae can be minimized by controlling light exposure to the water and maintaining proper nutrient levels.
- pH Fluctuations: Gradual adjustments using pH buffers can stabilize the water’s pH level without shocking the system’s inhabitants.
- Low Oxygen Levels: Additional aeration equipment or increasing the flow rate of existing aerators can help raise oxygen levels.
Regular maintenance, including cleaning filters and removing debris, will also help prevent water quality issues. In addition, establishing a routine testing schedule for water parameters allows for early detection and correction of any problems, ensuring the aquaponics system remains a thriving environment for both fish and plants.
Automation and Monitoring: Ensuring System Efficiency
Automated Feeding Systems
One of the cornerstones of an efficient aquaponics system is the automated feeding system. These systems ensure that fish are fed the optimal amount of food at regular intervals, which is crucial for maintaining their health and the balance of nutrients within the system. Automated feeders can be programmed to dispense food multiple times a day, reducing waste and ensuring consistency. This not only improves growth rates but also minimizes labor and the potential for human error.
Temperature and Light Control
Controlling the temperature and light within an aquaponics system is vital for both fish and plant health. Water heaters and chillers can be used to maintain the water at an ideal temperature for the fish species being farmed. Similarly, LED grow lights can be employed to provide plants with the necessary light spectrum for photosynthesis, especially in regions with insufficient natural sunlight. These systems can be automated and adjusted remotely, ensuring that the environment remains within the optimal range for system productivity.
Remote Monitoring Technologies
The advent of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies has revolutionized the monitoring and management of aquaponics systems. Sensors can now track a variety of parameters such as pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and nutrient levels. This data can be transmitted in real-time to a central management system or even to a mobile device, allowing for remote adjustments and instantaneous alerts if the system deviates from its desired state. This level of monitoring ensures that any issues can be addressed promptly, often before they become problematic, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency and productivity of the aquaponics system.
By integrating these automated systems and remote monitoring technologies, aquaponics can achieve higher levels of efficiency and productivity. These advancements not only reduce the need for manual labor but also increase the precision with which the systems are managed. As a result, aquaponics systems can operate more sustainably, with less impact on the environment and more consistent yields.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Energy-Efficient Equipment Choices
One of the cornerstones of a sustainable aquaponics system is the selection of energy-efficient equipment. The goal is to minimize energy consumption while maintaining optimal conditions for both fish and plants. Energy-efficient water pumps, LED grow lights, and solar-powered systems are examples of equipment that can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of an aquaponics setup. By choosing low-energy alternatives, growers not only contribute to environmental conservation but also benefit from reduced operational costs in the long term.
Reducing Water Usage
Aquaponics is renowned for its water efficiency, using up to 90% less water than traditional agriculture. However, there are still ways to enhance water conservation within the system. Techniques such as rainwater harvesting, recirculating water systems, and careful monitoring of water levels can further reduce water usage. Additionally, ensuring that the system is leak-proof and that evaporation is minimized through covers or greenhouse structures can contribute to water savings. These practices underscore the importance of water conservation in sustainable aquaponics operations.
Sourcing Sustainable Fish and Plant Varieties
The choice of fish and plants plays a significant role in the sustainability of an aquaponics system. Opting for native and adaptable fish species that require less energy for heating and cooling the water can lead to a more sustainable setup. Similarly, selecting plant varieties that are well-suited to the local climate and available nutrients can reduce the need for external inputs. By sourcing sustainable fish and plant varieties, growers can create a more eco-friendly system that supports local biodiversity and reduces the environmental impact of food production.
In conclusion, the sustainability and environmental impact of an aquaponics system are heavily influenced by the equipment choices, water usage practices, and the selection of fish and plant species. By focusing on energy efficiency, water conservation, and sustainable sourcing, aquaponics can serve as a model for environmentally responsible food production, offering a blueprint for future agricultural practices that prioritize the health of our planet.




