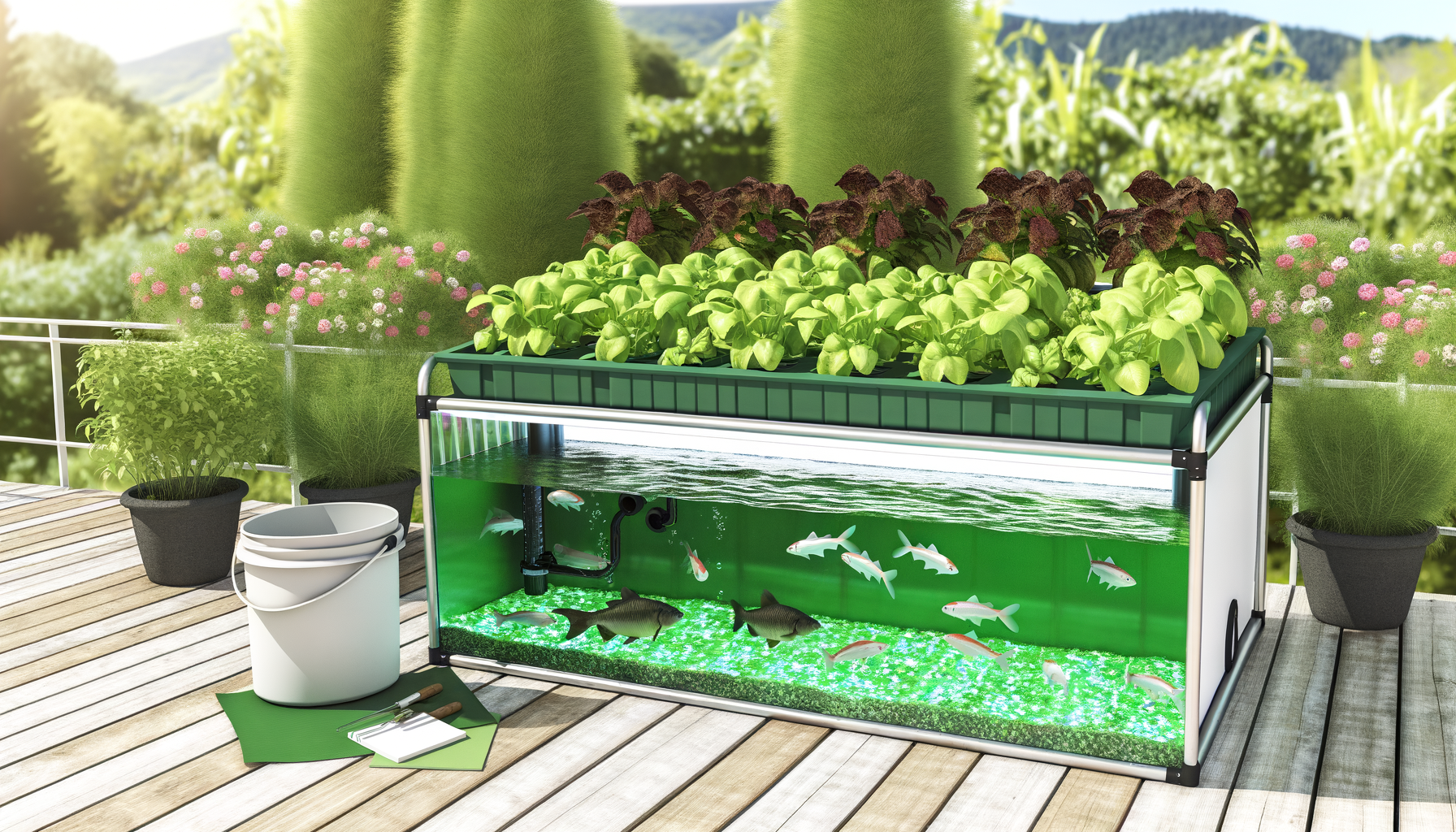
Introduction to Aquaponics
Understanding Aquaponics
Aquaponics is an innovative and sustainable method of farming that combines aquaculture (raising aquatic animals) with hydroponics (cultivating plants in water). This symbiotic system allows fish waste to serve as a natural fertilizer for the plants, while the plants, in turn, purify the water for the fish. It’s a closed-loop system that mimics natural ecological cycles, creating a harmonious environment for both fish and flora.
Benefits of Aquaponic Gardening
The advantages of aquaponic gardening are numerous. It is water-efficient, using up to 90% less water than traditional soil-based gardening since water is recirculated. Aquaponics is also space-efficient, allowing for higher yield in a smaller area, making it ideal for urban settings or areas with poor soil quality. Moreover, it is eco-friendly, eliminating the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, and can be energy-efficient when integrated with renewable energy sources.
Aquaponics vs. Traditional Gardening
Compared to traditional gardening, aquaponics presents a reduction in labor as there is no need for tilling, weeding, or soil management. It also offers faster plant growth and can be operated year-round in controlled environments. However, it does require an initial investment in equipment and a learning curve to manage the system effectively.
Aquaponics vs. Hydroponics
While both systems grow plants in water, aquaponics is a step ahead of hydroponics by incorporating fish into the equation. This creates a self-sustaining ecosystem where fish provide nutrients for the plants, and plants clean the water for the fish. Hydroponics, on the other hand, requires the addition of chemical nutrients to the water for plant growth, which can be costly and less environmentally friendly.
The Relevance of Aquaponics in Modern Agriculture
Aquaponics is gaining traction as a viable solution to modern agricultural challenges. It offers a way to produce food in urban areas, minimize the carbon footprint of food production, and conserve water in regions where it is scarce. As the world grapples with climate change and population growth, aquaponics stands out as a resilient farming method that can help ensure food security and sustainability.
Fundamentals of Aquaponic Systems
Key Components of Aquaponics
Aquaponics is an innovative and sustainable method of farming that combines aquaculture (raising aquatic animals) with hydroponics (cultivating plants in water). The key components of an aquaponic system include:
- Fish Tank: The habitat for the fish whose waste provides nutrients for the plants.
- Grow Bed: Where plants are cultivated, often filled with a growth medium that supports the plants and houses beneficial bacteria.
- Water Pump and Plumbing: Essential for circulating water between the fish tank and the grow bed.
- Air Pump: Provides oxygen to the fish and the root systems of the plants, crucial for their survival and growth.
- Beneficial Bacteria: These naturally occurring bacteria convert ammonia from fish waste into nitrates, which plants use as nutrients.
The Aquaponic Cycle Explained
The aquaponic cycle is a continuous loop that begins with the fish producing waste. This waste, containing ammonia, is pumped into the grow bed where bacteria convert it into nitrites and then nitrates. The plants absorb these nitrates as their primary nutrient source. The cleaned water, now devoid of waste, is recirculated back to the fish tank, creating a sustainable ecosystem.
Types of Aquaponic Systems
There are several types of aquaponic systems, each with its own advantages and challenges:
- Media Bed (Flood and Drain): Ideal for beginners, it uses a grow bed filled with media such as clay pebbles or gravel. The bed is periodically flooded with water from the fish tank.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): Suitable for growing leafy greens, it involves a thin film of water flowing through channels containing plant roots.
- Deep Water Culture (DWC): Plants float on water with their roots submerged, often used in commercial setups due to its scalability and efficiency.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Selecting the right aquaponic system depends on various factors, including space, budget, and the type of plants and fish you wish to cultivate. Consider the following:
- Space: The amount of available space will dictate the size of your system. Smaller systems are easier to maintain, while larger ones can yield more produce.
- Maintenance: Some systems require more cleaning and monitoring than others. Choose one that fits your lifestyle and availability.
- Energy Efficiency: Systems with additional components like heaters and lights will consume more energy. Balance your desire for energy efficiency with the needs of your plants and fish.
- Plant and Fish Choices: Not all systems are suitable for every type of plant or fish. Research which species will thrive in the system you are considering.
By understanding the fundamentals of aquaponic systems, you can make an informed decision on which setup will best suit your needs, leading to a successful and enjoyable aquaponic gardening experience.
Designing Your Aquaponics System
Planning Your Aquaponics Setup
Embarking on your aquaponics journey begins with careful planning. Start by determining the scale of your system based on available space and your desired yield. Consider the types of fish and plants you wish to cultivate, as these will influence the design of your system. Research local regulations regarding aquaculture, and ensure you have access to quality water and a reliable power source. It’s also essential to budget for initial setup costs and ongoing maintenance.
Constructing a Media Bed Aquaponic System
A media bed aquaponic system is a popular choice for beginners due to its simplicity and effectiveness. To construct one, you’ll need a fish tank, grow beds filled with a porous medium like expanded clay pebbles or gravel, and a water pump. The grow bed should be positioned above the fish tank, allowing water to flow back via gravity. A bell siphon or standpipe can be used to regulate the flood and drain cycles, ensuring the roots receive both nutrients and oxygen.
System Cycling and Management
Before introducing fish and plants, your system must undergo cycling to establish beneficial bacteria that convert fish waste into plant nutrients. This process, known as the nitrogen cycle, can take several weeks. During this time, monitor water parameters such as pH, ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates closely. Once the system is cycled, you can gradually add fish and plants, adjusting feeding rates and water flow to maintain a balanced ecosystem.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Water Quality Problems: Regular testing is crucial. If ammonia or nitrite levels rise, reduce feeding and consider adding more plants or a biofilter.
- Plant Growth Issues: Insufficient light or nutrient imbalances can hinder plant growth. Ensure adequate lighting and adjust fish stocking density or feeding rates as needed.
- Fish Health: Keep an eye out for signs of stress or disease in your fish. Maintain proper water temperature and quality, and quarantine new fish before adding them to the system.
- System Leaks: Regularly inspect all connections and fittings. Address leaks promptly to prevent water loss and potential damage to the system.
By anticipating and understanding these common issues, you can maintain a healthy and productive aquaponics system.
Stocking Your Aquaponics System
Selecting Compatible Fish Species
Choosing the right fish for your aquaponics system is crucial for the health and balance of your mini-ecosystem. Fish play a vital role in providing the nutrients plants need to grow. Some of the most popular and hardy species for aquaponics include Tilapia, Catfish, Koi, and Goldfish. These species are known for their adaptability, resilience, and rapid growth. When selecting fish, consider factors such as climate adaptability, growth rate, and how they interact with the plant varieties you intend to grow. It’s important to select species that thrive in your local climate to reduce the need for additional heating or cooling.
Choosing Plants for Your Aquaponics System
The plants you choose should be well-suited to the nutrient-rich water provided by your fish. Leafy greens like lettuce, kale, and spinach are excellent choices for beginners due to their low maintenance and quick harvest times. Herbs such as basil, mint, and chives also do well in aquaponic systems. For more experienced gardeners, fruiting plants like tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers can be rewarding but require more careful monitoring and balancing of the system. Always ensure that the plants you select are compatible with the water temperature and pH levels maintained by the fish species in your system.
Balancing Fish and Plant Populations
A balanced ratio of fish to plants is essential for a successful aquaponics system. Too many fish can lead to excessive waste, which can overwhelm the plants and lead to toxic ammonia levels. Conversely, too few fish may not provide enough nutrients for the plants. A general rule of thumb is to maintain a balance where the fish tank volume correlates to the grow bed volume at a 1:1 ratio. Regular testing of water quality parameters such as ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates will help you maintain the right balance and make adjustments as needed.
Feeding and Care for Aquaponic Fish
The health of your fish is paramount in an aquaponics system, as they are the nutrient source for your plants. Feed your fish high-quality aquaponic-specific feed to ensure they receive all the necessary nutrients. Overfeeding can lead to water quality issues, so it’s important to feed only as much as the fish can consume in about five minutes. Regular observation of fish behavior and health can alert you to potential problems early on. Keep in mind that the type of fish food, feeding frequency, and quantity will vary depending on the fish species and system size.
By carefully selecting compatible fish and plants, maintaining a balanced population, and providing proper care and feeding, your aquaponics system can flourish, providing you with fresh produce and a rewarding experience in sustainable gardening.
Maintaining Your Aquaponics System
Daily Maintenance Tasks
Maintaining a healthy aquaponics system requires regular attention. Daily tasks are crucial for the system’s stability and productivity. Begin by checking water levels to ensure pumps and filters are fully operational. Observe fish behavior for signs of stress or disease, and verify that they are feeding properly. Inspect plants for pests and diseases, and remove any dead leaves or debris. Test water pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels to maintain a balanced environment. Lastly, ensure that the system’s temperature is within the optimal range for both fish and plants.
Weekly Maintenance Checklist
- Inspect Equipment: Check all system components, including pumps, pipes, and aerators, for signs of wear or clogging.
- Clean Components: Remove any algae or biofilm buildup in pipes, tanks, and grow beds.
- Water Quality: Conduct a thorough water quality test and adjust as necessary to maintain the balance.
- Plant Health: Prune plants to promote growth and remove any that are not thriving.
- Fish Health: Monitor fish growth and health, and adjust feeding rates accordingly.
Monthly System Assessments
Monthly assessments involve a more in-depth analysis of your aquaponics system. Evaluate the overall system performance and growth rates of both fish and plants. Clean or replace filters and test backup systems to ensure they are functioning correctly. Record observations and any changes made to track progress and identify patterns that may require attention. This is also a good time to harvest mature plants and introduce new seedlings to keep the system productive.
Seasonal Adjustments and Maintenance
As seasons change, so do the needs of your aquaponics system. During spring and summer, increase aeration and water circulation to accommodate higher temperatures and plant growth rates. In fall, begin preparing for cooler weather by checking heating systems and insulating pipes if necessary. Winter may require additional heating and lighting to maintain optimal conditions. Adjust fish stocking levels and feeding schedules to match seasonal changes in growth rates. Finally, use this time to plan for the upcoming season, ensuring that your system continues to thrive year-round.
Regular maintenance is the key to a successful aquaponics system. By adhering to these daily, weekly, monthly, and seasonal tasks, you can ensure a productive and healthy environment for both your fish and plants. Remember, the more care and attention you give to your system, the more bountiful your harvest will be.
html
Optimizing Your Aquaponics System Location
Evaluating Space Requirements
Before setting up an aquaponics system, it’s crucial to assess the space available. The size of your system will depend on the area you can dedicate to it. Consider both the horizontal footprint and vertical space for plant growth. Ensure there is enough room for the fish tank, grow beds, and any additional equipment such as pumps or lighting. A compact system can fit on a small patio, while larger installations may require a dedicated greenhouse or outdoor area.
Maximizing Sunlight Exposure
Plants in an aquaponics system thrive with adequate sunlight. When choosing a location, aim for a spot that receives at least 6 to 8 hours of natural sunlight daily. If outdoor space is limited or sunlight is insufficient, artificial grow lights can supplement the light requirements. However, natural sunlight is preferable for its full spectrum and cost-effectiveness.
Proximity to Resources
Accessibility to water, electricity, and other resources is essential for the maintenance and operation of your aquaponics system. The system should be near a water source for easy top-offs and changes. Electrical outlets should be within reach for pumps and aeration systems. Additionally, consider the proximity to tools and storage for fish feed and other supplies.
Considerations for Heating and Insulation
Temperature control is vital for both fish and plant health. The system should be located in an area where the temperature can be maintained within the optimal range for your chosen species. In colder climates, this may mean placing the system indoors or adding heaters and insulation to an outdoor setup. Conversely, in hot climates, shading and cooling mechanisms may be necessary.
Safety and Accessibility
The system should be set up in a safe area, away from potential hazards such as chemicals or heavy foot traffic that could contaminate the water or damage the system. It should also be easily accessible for monitoring, feeding, and harvesting without the need for excessive bending or reaching, which can make maintenance tasks more laborious and time-consuming.
Conclusion and Further Exploration
Recap of Aquaponics Principles
Aquaponics is a sustainable and innovative farming method that combines aquaculture (raising fish) and hydroponics (soilless plant cultivation) in a symbiotic environment. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the essentials of aquaponics, including its benefits over traditional gardening and hydroponics, the key components of an aquaponic system, and the various types such as Gravel Bed Culture (GBC), Deep Water Culture (DWC), and Nutrient Film Technique (NFT). We’ve also discussed how to design, stock, and maintain your system to ensure a healthy and productive aquaponic garden.
The Future of Aquaponics
The future of aquaponics looks promising as it offers solutions to many of the challenges facing modern agriculture, such as water scarcity, land degradation, and the need for sustainable food production systems. With its ability to produce high-quality, organic food with minimal environmental impact, aquaponics is poised to play a significant role in urban farming, food security, and eco-friendly agricultural practices.
Additional Resources for Aquaponics Enthusiasts
- Books: “Aquaponics 101” provides a comprehensive beginner’s guide to aquaponic farming, covering system design, fish and plant selection, and maintenance.
- Websites: Websites like Aquaponics USA and CANNA UK offer valuable information, tutorials, and community support for aquaponic gardeners.
- Blogs: Blogs such as Affnan Aquaponics and Home Aquaponics Guide are excellent sources for tips, system designs, and personal experiences.
- Forums: Online forums and social media groups are great places to connect with other aquaponics enthusiasts, exchange ideas, and seek advice.
Encouragement for Ongoing Learning and Experimentation
As with any agricultural practice, aquaponics requires patience, learning, and experimentation. The journey from beginner to expert is filled with discoveries and challenges. Embrace the process, and don’t be discouraged by setbacks. Each failure is an opportunity to learn and improve. Remember, the most successful aquaponic systems are those that are well-researched, carefully monitored, and lovingly maintained. So, continue to expand your knowledge, experiment with different techniques, and share your experiences with the community. Your aquaponic garden is not just a source of food; it’s a living laboratory where you can witness the harmony of nature’s cycles firsthand.
Whether you aim to cultivate a small home garden or embark on a larger commercial venture, the principles of aquaponics will guide you towards a rewarding and environmentally conscious way of farming. Keep exploring, keep growing, and let your aquaponic journey contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.




